lv end diastolic pressure|end systolic volume : 2024-10-07 An elevated left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP) localizes pathology to the level of the left ventricle and provides a measure of preload, but it is important to recognize that the LVEDP and LA pressure provide complementary, but not interchangeable, information. Ostatné - Breitling bazár. Vyberajte z 9 inzerátov. Predaj ľahko a rýchlo na Bazoš.sk. Cez 400 tisíc užívateľov za deň.Op Chrono24 vindt u 47 Breitling Callisto horloges, kunt u prijzen van horloges vergelijken en daarna een horloge kopen, nieuw of tweedehands.
0 · what is end diastolic volume
1 · left end diastolic volume
2 · end systolic volume
3 · Meer
Bei 3 Uhr nimmt ein gut ablesbares weiß hinterlegtes Datumsfenster seinen Platz auf dem übersichtlichen grünen Zifferblatt ein. Die leistungsstarke Avenger Automatic ist wasserdicht .Op Chrono24 vindt u 41 Breitling Avenger Hurricane horloges, kunt u prijzen van horloges vergelijken en daarna een horloge kopen, nieuw of tweedehands.
lv end diastolic pressure*******An elevated left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP) localizes pathology to the level of the left ventricle and provides a measure of preload, but it is important to recognize that the LVEDP and LA pressure provide complementary, but not interchangeable, information.End-diastolic volume is the amount of blood in the left ventricle just before the heart contracts. It affects stroke volume, cardiac output, and heart function. Lear. As diastolic impairment progresses and LV compliance decreases, raised LV end-diastolic pressure increases LA afterload and therefore resistance to LA ejection, leading to a . Preload, also known as left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), measures the degree of the ventricular stretch when the heart is at the end of diastole.lv end diastolic pressure end systolic volumeLearn how to generate and interpret left ventricular pressure-volume (PV) loops from cardiac cycle diagrams. The PV loop shows the end-diastolic pressure and volume (EDPV) at the end of ventricular filling (diastole).Some studies used LV end-diastolic pressure as the gold standard (which is weakly related to Doppler indices of mean wedge pressure as E/e′), whereas others used LV pre–A-wave pressure, LV mean diastolic pressure, or .EDPVR (End-Diastolic Pressure-Volume Relationship) shows the relationship between ESV and left ventricular volume. The EDPVR curve shows that the left ventricle can withstand large pressure increases but at a certain threshold, .Therefore, LVDP at end-diastole is LVEDP, is measured at the “z” point and occurs in an average time of 0.052 sec after onset of the QRS of the electrocardiogram. Left ventricular diastolic .end systolic volume Both LA mean pressure and LV end-diastolic pressure are used to represent LV filling pressure, but the latter should be preferred when the focus of the study is LV . Every left ventricle has an intrinsic and limited range of possible volumes at end diastole. There is a curvilinear relationship between left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) and LV end-diastolic . To evaluate the left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP) in patients with diastolic heart failure by echocardiography and explore the clinical value of echocardiography. . LV pre-A-wave. [11,12,23,24,25] In this study, the average correlation coefficient between E/e’ and LVEDP was r = 0.367. The term LV filling pressure refers to the pressure that fills the left ventricle and is used differently depending upon which pressure is available. Both LA mean pressure and LV end-diastolic pressure are used to represent LV filling pressure, but the latter should be preferred when the focus of the study is LV mechanical function.The slope of the LV end-diastolic pressure-volume relation indicates the passive chamber stiffness. Since the relation is exponential in shape, the slope (ΔP/ΔV) increases as the end-diastolic pressure increases. From Little WC. Diastolic dysfunction beyond distensibility: adverse effects of ventricular dilatation. Circulation 2005;112:2888 .
A reduction in ventricular compliance, as occurs in ventricular hypertrophy, increases the slope of the ventricular end-diastolic pressure-volume relationship (EDPVR) and results in less ventricular filling (decreased end-diastolic volume) and a greater end-diastolic pressure (elevated pulmonary capillary wedge pressures) as shown in the figure (red loop).
This is unacceptable given the large day-to-day LVFP variations. Some studies used LV end-diastolic pressure as the gold standard (which is weakly related to Doppler indices of mean wedge pressure as E/e′), whereas others used LV pre–A-wave pressure, LV mean diastolic pressure, or wedge pressure. End-diastolic volume is how much blood is in the ventricles after the heart fills up with blood, but before it contracts to pump the blood around the body. Doctors use end-diastolic volume to .
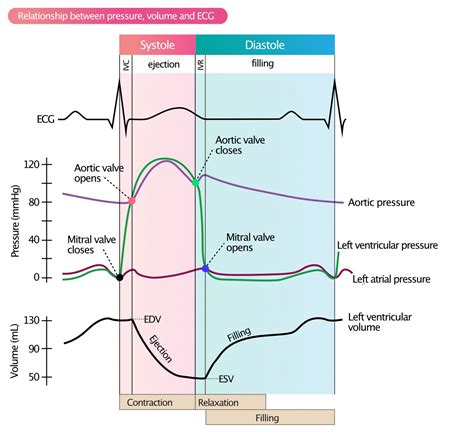
For these reasons, LVEDP continues to be a frequently utilized parameter in the assessment of ventricular performance. In patients with LV dysfunction, if ventricular filling pressure is utilized to assess LV performance, it is better to use LVEDP rather than an indirect estimate of LVEDP for the following reasons: 1) by using an indirect estimate of LVEDP the contribution of atrial .Increased LV end-diastolic pressure at rest or during exertion. Usually, normal LV end-diastolic volume. Global contractility and hence ejection fraction remain normal (≥ 50%). However, in some patients, marked restriction to LV filling can cause inappropriately low LV end-diastolic volume and thus cause low CO (cardiac output) and systemic . Background: Elevated left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP) may be caused by multiple etiologies, including myocardial ischemia due to obstructive coronary artery disease. Microvascular coronary dysfunction (MCD) can also lead to ischemia. The relationship between MCD and elevated LVEDP has not been previously described. Methods: We . 1. Introduction. Left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF) and LV end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes (LVEDV and LVESV, respectively) are commonly used as clinical parameters reflecting global LV systolic performance or LV remodeling [1, 2].Of note, compared with LVEF or LVEDV, previous reports emphasized the superiority of LVESV (or LVESV .lv end diastolic pressure Left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) is an important measure of ventricular performance and may identify patients at increased risk for developing late clinical symptoms of heart failure (HF). The primary outcome in this analysis of 744 patients from the Survival and Ventricular Enlargeme .Point 1 on the PV loop is the pressure and volume at the end of ventricular filling (diastole) and therefore represents the end-diastolic pressure and end-diastolic volume (EDV) for the ventricle. As the ventricle begins to contract .
The gold standard for determining LV filling pressures, is performed invasively by measuring the left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) via cardiac cath. Another method is by the pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP), .This is unacceptable given the large day-to-day LVFP variations. Some studies used LV end-diastolic pressure as the gold standard (which is weakly related to Doppler indices of mean wedge pressure as E/e′), whereas others used LV pre–A-wave pressure, LV mean diastolic pressure, or wedge pressure.Diastolic function and echocardiographic assessment. The importance of systolic function can be understood on an intuitive basis. Consider the fact that the left ventricle contracts and ejects blood into the aorta roughly 100,000 times daily, each time overcoming the aortic resistance, which is typically 110 mmHg or more.

To evaluate the left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP) in patients with diastolic heart failure by echocardiography and explore the clinical value of echocardiography.. From July 2017 to January 2018, 120 patients were prospectively selected from the affiliated hospital of Jiangsu university diagnosed as diastolic heart failure (York Heart Association class ≥II, LVEF ≥50%). Thus, LA pressure can be elevated, but LA reservoir strain can still fall in the normal range in patients with preserved LV long-axis systolic function. Likewise, LA pump strain has an inverse relation with LV end-diastolic pressure, but again, other parameters determine LA pump strain aside from filling pressures, particularly LA systolic . If a patient exhibited moderate LV enlargement (end-diastolic diameter of 65 mm or end-diastolic volume of 130 mL/m 2), an EF of 30%, a regurgitant fraction of 50%, and a regurgitant volume of 20 mL/m 2, the ratio of regurgitant volume to end-diastolic volume would be only 20/130, or 0.15.
Serial numbers on Breitling watches serve as indicators of the time and place of manufacture and are typically found on the case back of most watches. In addition to the serial number, each watch is also assigned a .
lv end diastolic pressure|end systolic volume






